Capacitors, Electronic Components, Electronics Tutorials
Electronics Tutorials: Reading capacitor values
One of the skills you’ll need if you are interested into electronics is reading capacitor values. In this post we’ll cover the different kinds of marking you can find in different capacitor types and how to read them.
Capacitor code calculator
If you are in a hurry or just want to check if you’ve read a code correctly, just type the code and hit “Calculate” to get the capacitor value in the most common units.
Capacitor values: Capacitance and Tolerance
Capacitance and capacitor properties are marked in the enclosure. The only problem is that depending on the capacitor type and size the marking code will differ, so you’ll need to get used to the different types of capacitor and how they are marked. These are the most common ones:
Types of Capacitors
Electrolytic capacitors
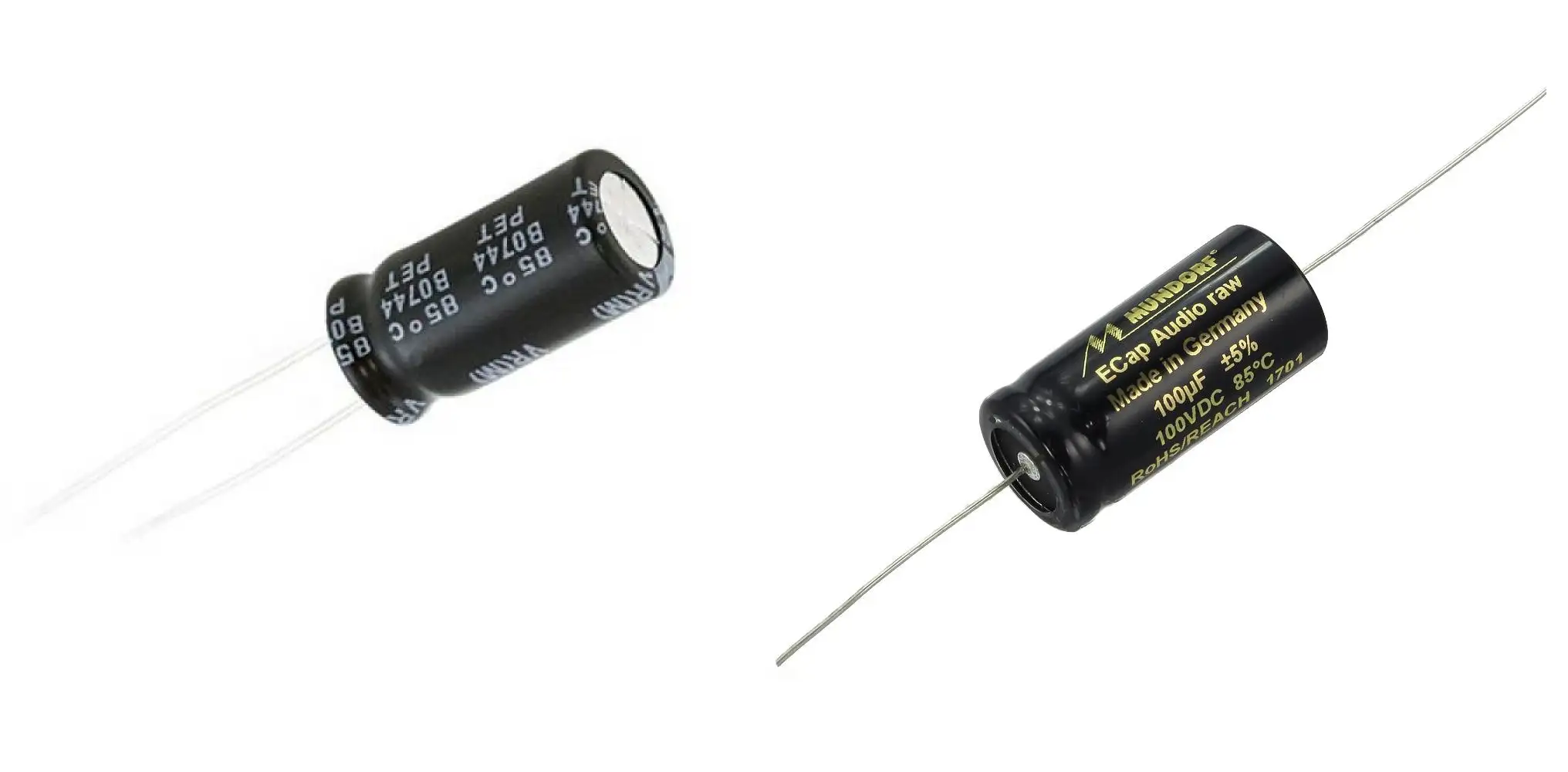

Electrolytic capacitors are the easiest to read: their value and maximum voltage is written directly in the enclosure. The capacitance is usually written in uF, but that’s not a problem as the unit is written along with the value. Let’s check a real world example:
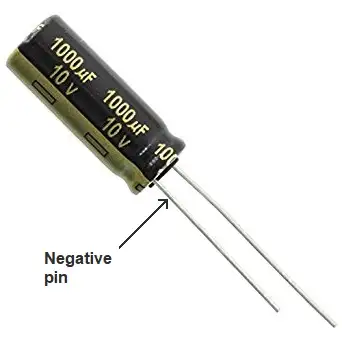
The value is 1000uF, and the maximum voltage rating 10V. Thanks to the marking in the case you can also know which one is the negative pin of the capacitor (-), that will have to be tied to the most negative part of the circuit. Remember that electrolytic capacitors have a polarity that must be respected carefully when connecting them in your circuits!
Polyester

Polyester capacitors have no polarity, and the values are written with a special notation. The capacitance marking consists on three numbers X, Y and Z
The total capacitance is calculated by taking the first two numbers and adding the number of zeros of the last number. The result is given in pF, so a conversion is often convenient.
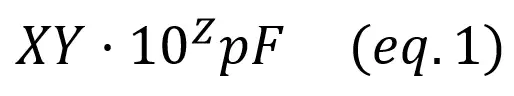
The maximum voltage is given by a letter:
– 0J: 6.3V
– 1A: 10V
– 1C: 16V
– 1E: 25V
– 1H: 50V
– 2A: 100V
– 2D: 200V
– 2E: 250V
The tolerance is also given by a letter. These are the letter codes for capacitor tolerances:
F: +/- 1%
G: +/- 2%
J: +/- 5%
K: +/- 10%
M: +/- 20%
Let’s review all of this with an example:
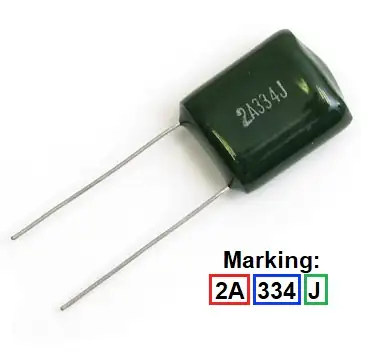
Value (blue box): 334 → 330nF
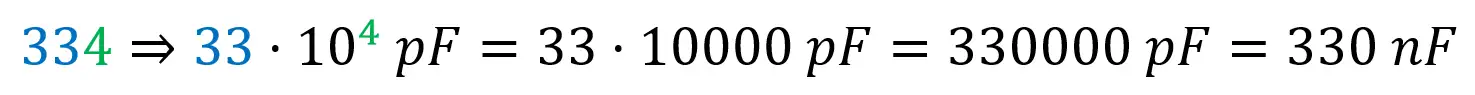
Tolerance: 5%
Voltage: 100V
Ceramic capacitors

Ceramic capacitors are even smaller and usually only the capacitance value is marked, and, like polyester ones, are non-polarized. Maximum voltage is quite high (50V or more), and capacitance is 10% for standard E12 series capacitors. The code used is the same as for polyester capacitors:
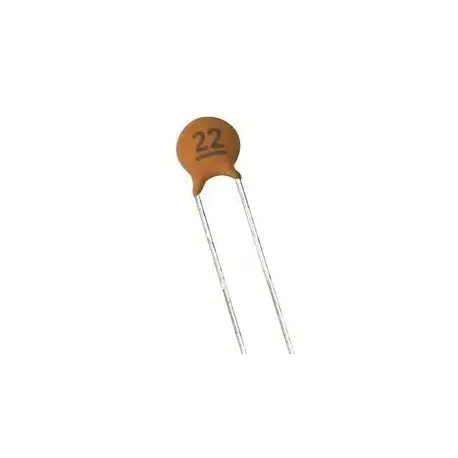

Value: 22 → 22pF
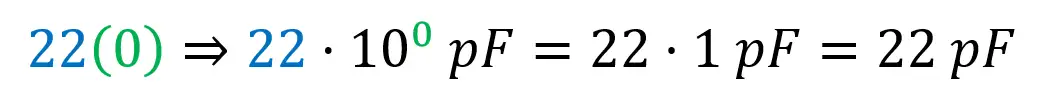
Tolerance, as it happens in this case, might not appear in the marking.
